Abstract
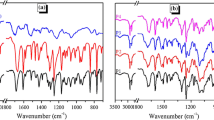
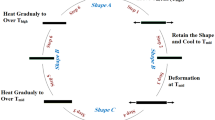
In order to better understand the interrelation between liquid crystal fillers and functional polymers, a series of liquid crystalline shape memory polyurethane composites (LC-SMPUCs), named shape memory polyurethane (SMPU)–4-hexadecyloxybenzoic acid (HOBA) composites, are prepared by incorporating HOBA into SMPU based on a polyethylene glycol (PEG) soft segment. The results demonstrate that the dimerization structure of HOBA is maintained in the as-prepared SMPU–HOBA composites, facilitating liquid crystalline properties. Characterization results display smectic C phase upon heating, while the isotropic temperature shifts to a higher temperature, broadening the temperature range of the liquid crystalline phase. The SMPU–HOBA composites form a two-phase separated structure containing a SMPU phase and a HOBA phase; the incorporated HOBA can promote crystallizability of both soft and hard segments of SMPU, while crystalline hard phases are maintained within the high temperature range. Thus, SMPU–HOBA composites demonstrate a two-step modulus change upon heating that releases a triple-shape memory effect. The final shape fixing ratio is higher than 99%, and the final shape recovery ratio reaches 90%. Therefore, the SMPU–HOBA composites successfully provide a desirable combination of liquid crystalline properties and triple-shape memory properties, making them ideal candidates for smart sensor, smart labels, etc.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao Q, Qi HJ, Xie T (2015) Recent progress in shape memory polymer: new behavior, enabling materials, and mechanistic understanding. Prog Polym Sci 49–50:79–120
Hager MD, Bode S, Weber C, Schubert US (2015) Shape memory polymers: past, present and future developments. Prog Polym Sci 49–50:3–33
Liu YJ, Du HY, Liu LW, Leng JS (2014) Shape memory polymers and their composites in aerospace applications: a review. Smart Mater Struct 23(2):023001
Meng H, Li G (2013) A review of stimuli-responsive shape memory polymer composites. Polymer 54:2199–2221
Kumar KSS, Biju R, Nair CPR (2013) Progress in shape memory epoxy resins. React Funct Polym 73:421–430
Sun L, Huang WM, Ding Z, Zhao Y, Wang CC, Purnawali H, Tang C (2012) Stimulus-responsive shape memory materials: a review. Mater Des 33:577–640
Lu HB, Lu CR, Huang WM, Leng JS (2015) Chemo-responsive shape memory effect in shape memory polyurethane triggered by inductive release of mechanical energy storage undergoing copper (II) chloride migration. Smart Mater Struct 24(7):035018–035018
Singhal P, Small W, Cosgriff-Hernandez E, Maitland DJ, Wilson TS (2014) Low density biodegradable shape memory polyurethane foams for embolic biomedical applications. Acta Biomat 10:67–76
Ronda JC, Del Rio E, Lligadas G, Galia M, Cadiz V, Meier M (2011) Shape memory polyurethanes from renewable polyols obtained by ATMET polymerization of glyceryl triundec-10-enoate and 10-undecenol. Macromol Chem Phy 212:1392–1399
Ji FL, Hu JL, Han JP (2011) Shape memory polyurethane-ureas based on isophorone diisocyanate. High Perform Polym 23:177–187
Zhang YM, Wang C, Pei XQ, Wang QH, Wang TM (2010) Shape memory polyurethanes containing azo exhibiting photoisomerization function. J Mater Chem 20:9976–9981
Zhang DW, Liu YJ, Leng JS (2010) Magnetic field activation of thermoresponsive shape-memory polymer with embedded micron sized Ni powder. Adv Mater Res 123–125:995–998
Zhang DW, Leng JS, Liu YJ (2008) Influence of radialization dosage on shape memory effect of polystyrene copolymer. Adv Mater Res 47–50:690–693
Li L, Li Y, Li JS, Yao L, Mak A, Ko F, Qin L (2008) Antibacterial and nontoxic nano silver PLLA composites for tissue engineering. Adv Mater Res 47–50:849–852
Lan X, Leng JS, Liu YJ, Du SY (2008) Investigate of electrical conductivity of shape-memory polymer filled with carbon black. Adv Mater Res 47–50:714–717
Golbang A, Kokabi M (2010) Magnetic Field Actuation of shape Memory Nanocomposites. Adv Mater Res 123–125:999–1002
Sun L, Huang WM, Wang CC, Ding Z, Zhao Y, Tang C, Gao XY (2014) Polymeric shape memory materials and actuators. Liq Cryst 41:277–289
Kasi RM, Ahn SK, Deshmukh P, Gopinadhan M, Osuji CO (2011) Side-chain liquid crystalline polymer networks: exploiting nanoscale smectic polymorphism to design shape-memory polymers. ACS Nano 5:3085–3095
Hiraoka K, Tashiro T, Kobayashi M, Kazama R, Sagano W (2010) Symmetry and stimulus response of chiral smectic liquid-crystalline elastomers. In: Khoo IC (ed) Proceedings of SPIE, liquid crystals XIV, California, 1–2 and 4 August 2010
Finkelmann H, Happ M, Portugal M, Ringsdorf H (1978) Liquid-crystalline polymers with biphenyl-moieties as mesogenic group. Macromol Chem Phy 179:2541–2544
Sonin AS, Churochkina NA, Kaznacheev AV (2008) Polymer liquid crystalline composite for optical irradiation control. Polym Sci Ser B 50:30–34
Ahir SV, Tajbakhsh AR, Terentjev EM (2006) Self-assembled shape-memory fibers of triblock liquid-crystal polymers. Adv Funct Mater 16:556–560
Chen SJ, Yuan HM, Zhuo HT, Chen SG, Yang HP, Ge ZC, Liu JH (2014) Development of liquid-crystalline shape-memory polyurethane composites based on polyurethane with semi-crystalline reversible phase and hexadecyloxybenzoic acid for self-healing applications. J Mater Chem C 2:4203–4212
Chen SJ, Yuan HM, Ge ZC, Chen SG, Zhuo HT, Liu JH (2014) Insights into liquid-crystalline shape-memory polyurethane composites based on an amorphous reversible phase and hexadecyloxybenzoic acid. J Mater Chem C 2:1041–1049
Chen SJ, Yuan HM, Chen SG, Yang HP, Ge ZC, Zhuo HT, Liu JH (2014) Development of supramolecular liquid-crystalline polyurethane complexes exhibiting triple-shape functionality using a one-step programming process. J Mater Chem A 2:10169–10181
Chen SJ, Mo FN, Chen SG, Ge ZC, Yang HP, Zuo JD, Liu XK, Zhuo HT (2015) New insights into multi-shape memory behaviours and liquid crystalline properties of supramolecular polyurethane complexes based on pyridine-containing polyurethane and 4-octyldecyloxybenzoic acid. J Mater Chem A 3:19525–19538
Ban J, Zhu L, Chen SJ, Wang YP (2016) The impact of liquid crystal fillers on structure and properties of liquid-crystalline shape-memory polyurethane composites I: 4-dodecyloxybenzoic acid. J Mater Sci 51:10229–10244. doi:10.1007/s10853-016-0251-7
Mo FN, Zhou FX, Chen SJ, Yang HP, Ge ZC, Chen SG (2015) Development of shape memory polyurethane based on polyethylene glycol and liquefied 4,4 ‘-diphenylmethane diisocyanate using a bulk method for biomedical applications. Polym Int 64:477–485
Nosikova LA, Kudryashova ZA, Iskhakova LD, Tsivadze AY (2007) Solid-phase polymorphism of p-n-hexyloxy- and p-n-heptyloxybenzoic acids. Russ J Phys Chem A 81:1263–1266
Shatalova AM, Kresse H, Shandryuk GA, Bondarenko GN, Kuptsov SA, Talroze RV (2004) The role of the alien proton acceptor on the formation of LC structure in H-bonded monomeric and polymeric derivatives of alkoxybenzoic acids. J Mol Struct 708:7–14
Chen H, Liu Y, Gong T, Wang L, Zhao K, Zhou S (2013) Use of intermolecular hydrogen bonding to synthesize triple-shape memory supermolecular composites. RSC Adv 3:7048–7056
Zhu Y, Hu J, Choi K-F, Meng Q, Chen S, Yeung K-W (2008) Shape memory effect and reversible phase crystallization process in SMPU ionomer. Polym Adv Technol 19:328–333
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61425007, 61377090, and 61575128), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (Grant Nos. 2014A030313559, 2016A030313050), the Special Research Foundation of Shenzhen Overseas High-level Talents for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Grant No. KQCX20120807153115869), the Nanshan District Key Lab for Biopolymers and Safety Evaluation (No. KC2014ZDZJ0001A), the Science and Technology Project of Shenzhen City (Grant Nos. JCYJ20140828163633993, ZDSYS201507141105130, CYZZ20150827160341635).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ban, J., Zhu, L., Chen, S. et al. The effect of liquid crystal fillers on structure and properties of liquid crystalline shape memory polyurethane composites II: 4-hexadecyloxybenzoic acid. J Mater Sci 52, 2628–2641 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0554-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0554-8